Smart Ways to Optimize your Gastroparesis Diet for Better Digestion in 2025
Smart Ways to Optimize Your Gastroparesis Diet for Better Digestion in 2025
Understanding the Gastroparesis Diet
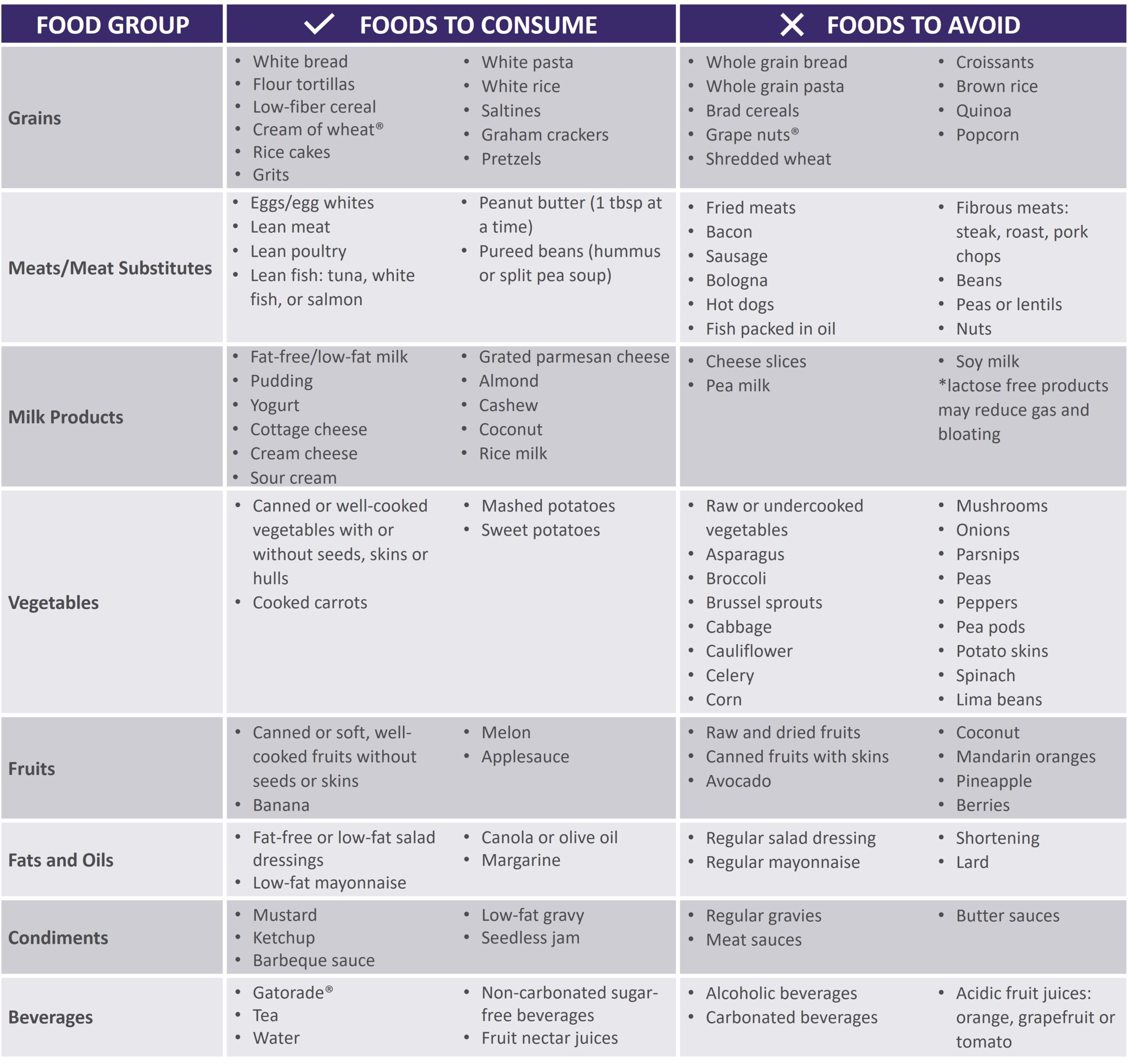
Living with gastroparesis poses unique challenges, particularly regarding dietary management. The essence of a **gastroparesis diet** revolves around making informed choices that enhance digestion while minimizing symptoms. This condition affects the stomach’s ability to empty properly, making **low-fiber diets** and **small frequent meals** vital strategies. These approaches help reduce the workload on the digestive system. In this section, we will discuss essential dietary adjustments, including focusing on **easy-to-digest foods** and maintaining **hydration strategies** to promote gastrointestinal health.
Essentials of a Low-Fiber Diet
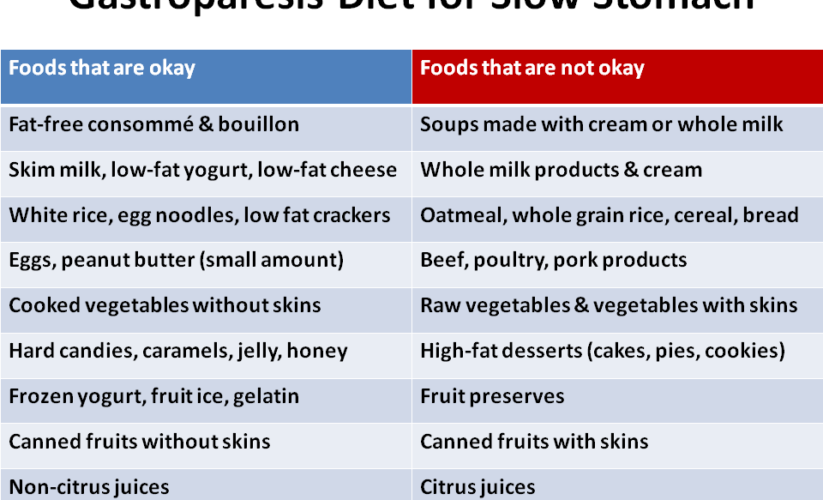
When managing gastroparesis, adopting a **low-fiber diet** is particularly beneficial as high-fiber foods can further slow gastric emptying. Fiber restrictions are often recommended, and it is advisable to choose **soft foods** that less-occlude the digestive tract. Focus primarily on refined grains, cooked vegetables, and select fruits that offer a gentle approach to digestion. For instance, opting for white rice or cooked carrots can provide the necessary nutrients without overwhelming the stomach. **Liquid nutrition** alternatives, such as smoothies or **meal replacement shakes**, can also be advantageous, as they are typically easier for the body to absorb.
The Importance of Meal Frequency Adjustments
Adopting **meal frequency adjustments** is crucial for individuals with gastroparesis. Spreading nutrient intake throughout the day into **low-volume meals** enables easier digestion and reduces the discomfort associated with larger meals. Aim for five to six small meals, focusing on nutrient-dense options scattered over time. This approach enhances nutrient absorption while minimizing symptoms. Foods to avoid include those that are high in fat, which can delay gastric emptying, thus exacerbating the discomfort. Instead, prioritize hydration and consider **electrolyte-rich foods** to maintain balance and fend off fatigue.
Tailored Meal Plans For Better Digestion
Creating a **tailored meal plan** allows for the integration of personal dietary goals with the unique challenges presented by gastroparesis. The optimal approach involves not only tracking food intake but also being aware of **food triggers** that may lead to exacerbations. Engaging with a registered dietitian can be immensely beneficial; they can assist in recognizing symptoms and developing recipes that align with individual preferences and tolerances, from low-carb meals to **digestion-friendly snacks**. This personalization fosters adherence to the diet and encourages a balanced intake that focuses on essential nutrients.
Nutritional Therapy and Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating **nutritional therapy** and making specific **lifestyle modifications** can greatly enhance overall health in individuals with gastroparesis. These strategies not only focus on dietary changes but also on developing a holistic routine that supports well-being and helps manage symptoms. In the following sections, we will explore the incorporation of anti-inflammatory foods, how to reduce food triggers, and the role of cooking techniques in meal preparation for those dealing with sensitive digestion.
Integrating Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Incorporating **anti-inflammatory foods** into your meal plan can help mitigate some symptoms associated with gastroparesis. Foods such as oily fish, nuts, and leafy greens provide ample nutrients while resisting the effects of inflammation on our digestive system. Preparing dishes with herbs like turmeric and ginger can also serve as a powerful means of promoting digestion and alleviating nausea. Focus on **nutritious smoothies** blended with spinach and protein sources to elevate nutritional content without the concern of abrasive digestion.
Culinary Strategies for Cooking with Gastroparesis
Utilizing appropriate **cooking methods** is pivotal when preparing meals for gastroparesis. Techniques such as steaming, baking, or pureeing help maintain nutritional content while making food easier to digest. Implementing a variety of **soft texture recommendations**—like mashed potatoes or blended soups—can create satisfying meals that don’t compromise gastrointestinal health. **Cooking gadgets for easy meals**, such as slow cookers or blenders, can simplify meal prep and ensure consistent adherence to cooking strategies better suited for sensitive digestion.
Effective Hydration Strategies
Hydration is an integral component of dietary management for gastroparesis. Individuals must ensure they are consuming sufficient fluids throughout the day to aid digestion while controlling electrolyte levels. Opt for **lactose-free options**, herbal teas, and broth-based soups, which allow for hydration while being gentle on the stomach. Additionally, staying attentive to **hydration importance** helps alleviate feelings of fullness that can accompany meals.
Meal Preparation and Planning Techniques
Planning meals in advance can significantly streamline the management of gastroparesis symptoms. By adopting effective meal preparation strategies, individuals can avoid the last-minute stress of figuring out what to eat, allowing for healthier choices that support digestive well-being. In this section, we’ll review practical tips for **creating a meal schedule**, selecting **food consistency recommendations**, and navigating social situations while maintaining dietary integrity.
Creating a Meal Schedule For Consistency
Maintaining a consistent **meal schedule** encourages better digestion by regulating the body’s natural rhythm. Aim to set specific times for meals and incorporate small snacks as needed. Tracking food intake can help evaluate which meals trigger symptoms and guide necessary adjustments. By being proactive with a set meal time, one can systematically approach **managing gastroparesis symptoms** through structured guideline adherence and accountability.
Portion Control Techniques for Dietary Success
Practicing appropriate **portion control techniques** can be immensely helpful in avoiding overwhelm during meals. Utilizing smaller plates, serving controlled portions, and preparing low-volume meals can lead to better outcomes. For effective **meal portion control**, even measuring out food can help resist the temptation to overeat. Staying in tune with one’s body can also aid in understanding food tolerance levels and thus mitigate adverse reactions.
Tips for Navigating Social Situations
Navigating social situations can be challenging when managing a gastroparesis diet. One strategy is to communicate dietary restrictions in advance when attending gatherings or dining out. Seeking out restaurants that offer **gluten-free options** or **lactose-free choices** can facilitate better management of dietary needs away from home. To feel more comfortable, consider bringing your own **easy-to-digest foods** or snacks to ensure you have suitable options available while being surrounded by tempting alternatives.
Key Takeaways
- Implement a **low-fiber diet** focusing on soft, easy-to-digest meals.
- Adjust meal frequency and portion control for better symptom management.
- Consider **nutritional therapy** and personalized meal planning for optimal nutrition.
- Emphasize hydration, anti-inflammatory foods, and mindful cooking techniques.
- Be proactive in maintaining a consistent meal schedule and navigate social situations with strategic planning.
FAQ
1. What are the best soft food options for a gastroparesis diet?
**Soft food options** for a gastroparesis diet include mashed potatoes, applesauce, smoothies, and broths. These foods are gentler on the digestive system, making them easier to digest while providing necessary nutrients.
2. How can I ensure proper hydration on a gastroparesis diet?
Maintaining hydration involves consuming fluids such as herbal teas, electrolytic drinks, and broth-based soups. Incorporate these into your daily routine and spread fluid intake throughout the day to support digestive function.
3. What are some **high-protein diet** choices suitable for gastroparesis?
**High-protein options** suitable for this diet include pureed lentils, yogurt, eggs (well-cooked), and protein shakes. Many protein-rich foods can be made easier to digest through cooking or blending.
4. How can tracking food intake help manage gastroparesis symptoms?
Tracking food intake allows you to identify patterns in how your body responds to different foods. Understanding which items trigger symptoms can lead to better dietary decisions and symptom management over time.
5. What role do **vitamin supplements** play in a gastroparesis diet?
Given the risk of nutrient deficiencies in gastroparesis patients, introducing **vitamin supplements** may be necessary to cover any gaps in essential nutrients. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
6. How can I manage gastroparesis symptoms while dining out?
To manage symptoms while dining out, research restaurants with favorable **bland food options** beforehand, and communicate your dietary needs clearly. Bringing your own snacks can also ease concerns about finding appropriate food.
7. What are the benefits of **meal replacement shakes** for gastroparesis patients?
**Meal replacement shakes** can be beneficial as they provide a concentrated source of vitamins and minerals in an easily digestible form. They can help ensure adequate nutrient intake without overwhelming the stomach.
By optimizing your gastroparesis diet with strategic choices and practical adjustments, you can significantly improve your digestion and overall quality of life in 2025.