Smart Ways to Optimize Your Hypoglycemia Diet in 2025: Discover Effective Strategies!
Smart Ways to Optimize Your Hypoglycemia Diet in 2025
In 2025, optimizing your hypoglycemia diet is crucial for managing symptoms and promoting overall health. This article will explore effective strategies for creating a hypoglycemic meal plan, discuss the importance of specific nutrients, and provide guidelines for meal planning. By understanding your nutritional needs and implementing thoughtful approaches, you can maintain balanced blood sugar levels and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Understanding Hypoglycemia and Its Dietary Management
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, occurs when glucose levels fall below normal limits. Proper dietary management of hypoglycemia plays a fundamental role in preventing episodes. A well-structured low blood sugar diet emphasizes the importance of understanding the glycemic index (GI) of foods consumed. Foods with a low glycemic index are absorbed slowly, preventing rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. Incorporating such options into a hypoglycemic meal plan can significantly reduce the risk of symptom recognition and promote better overall health.
The Role of Glycemic Index Foods
Oftentimes when managing hypoglycemia, it is essential to focus on foods for hypoglycemia that have a low glycemic index. Low GI foods include whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables. These foods help in stabilizing blood sugar levels by slowly releasing glucose into the bloodstream. For example, brown rice and quinoa are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates for stable blood sugar, which is beneficial for maintaining energy levels throughout the day. Additionally, consuming high fiber foods for blood sugar control can aid in improving digestion and prolonging satiety.
Diverse Nutritional Needs for Hypoglycemics
A well-balanced hypoglycemia diet should incorporate various food groups to meet the nutritional needs of an individual. Proteins are essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels; thus, including proteins for hypoglycemia such as nuts, fish, and chicken in your daily meals will benefit energy stabilization. A varied diet rich in vitamins for blood sugar regulation, including antioxidant-rich berries and dark leafy greens for hypoglycemia, can provide nutritional balance and promote dietary diversity. Ensuring a diet abundant in whole foods for blood sugar will help manage symptoms and improve overall wellness.
Meal Frequency and Timeliness
Establishing a consistent eating schedule is paramount in managing hypoglycemia effectively. The eating schedule for hypoglycemia often includes frequent meals spread throughout the day. This approach helps prevent long gaps without food, which could lead to low blood sugar episodes. Meal preparation and planning meals for low blood sugar should account for portion sizes and ensure inclusivity of heart-healthy fats for blood sugar stabilization. Meal timing also plays a crucial role in avoiding sugar spikes; planning meals around your activities and individual needs will enable better glucose management.
Practical Strategies for Meal Preparation
Implementing practical meal prep for hypoglycemia techniques can simplify your diet management. Prepping snacks and meals in advance promotes better food choices during busy routines. Healthy snacks for low blood sugar should include protein snacks—like yogurt and air-popped popcorn—to avoid hunger bouts. Focusing on low-sugar recipes, meal replacement options, and utilizing food tracking apps can help maintain dietary guidelines. Additionally, learning basic cooking skills ensures that you can adapt recipes to fit your low glycemic index diet.
Quick Meal Ideas for Busy Lifestyles
For those with hectic schedules, creating quick meals for hypoglycemics can facilitate healthy eating without added stress. Consider dishes that incorporate complex carbohydrates, like whole-grain wraps filled with lean turkey and fresh spinach or a quinoa salad topped with almonds and assorted vegetables. Preparing batch meals, such as stir-fries or vegetable soups, can yield easy leftovers for lunches. Incorporating snacks strategically into your day—perhaps a handful of nuts or a low-fat cheese with whole grain crackers—ensures you’re sufficiently fueled while managing your condition effectively.
Staying Hydrated for Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Hydration and blood sugar levels are intricately linked, making it vital to stay hydrated throughout the day. Dehydration can negatively impact blood sugar regulation and increase the risk of experiencing hypoglycemia symptoms. Aim to consume plenty of water, herbal teas, or plain water-flavored drinks throughout your day. Ensuring hydration not only supports crucial metabolic functions but also eliminates confusion regarding thirst-related eating. Staying informed while consulting a dietitian can further enhance your understanding of the intersection between hydration and managing hypoglycemic episodes.
Mindful Eating and Grazing Strategy
Mindful eating for hypoglycemia is a technique that emphasizes personal connection and attentiveness to your food consumption. By implementing a grazing strategy for hypoglycemia, which involves eating smaller portions more frequently, you can foster a better relationship with food while managing your blood sugar levels. Engaging all senses during meals, such as paying attention to flavors, textures, and aromas, can improve awareness of food portions and emotional responses associated with your diet. Understanding your body’s hunger cues fosters healthier eating habits and combats sugar spikes.
Addressing Common Challenges in Hypoglycemia Management
Living with hypoglycemia presents various challenges that can affect dietary management. Understanding hypoglycemia is an essential first step; education about its symptoms and causes allows individuals to proactively manage their conditions. This includes consulting health professionals for personalized nutrition and stress management techniques tailored to one’s specific needs. Strategies for gradual sugar reduction can play a vital role in enhancing dietary choices that contribute positively to long-term health.
Recognizing and Responding to Hypoglycemic Symptoms
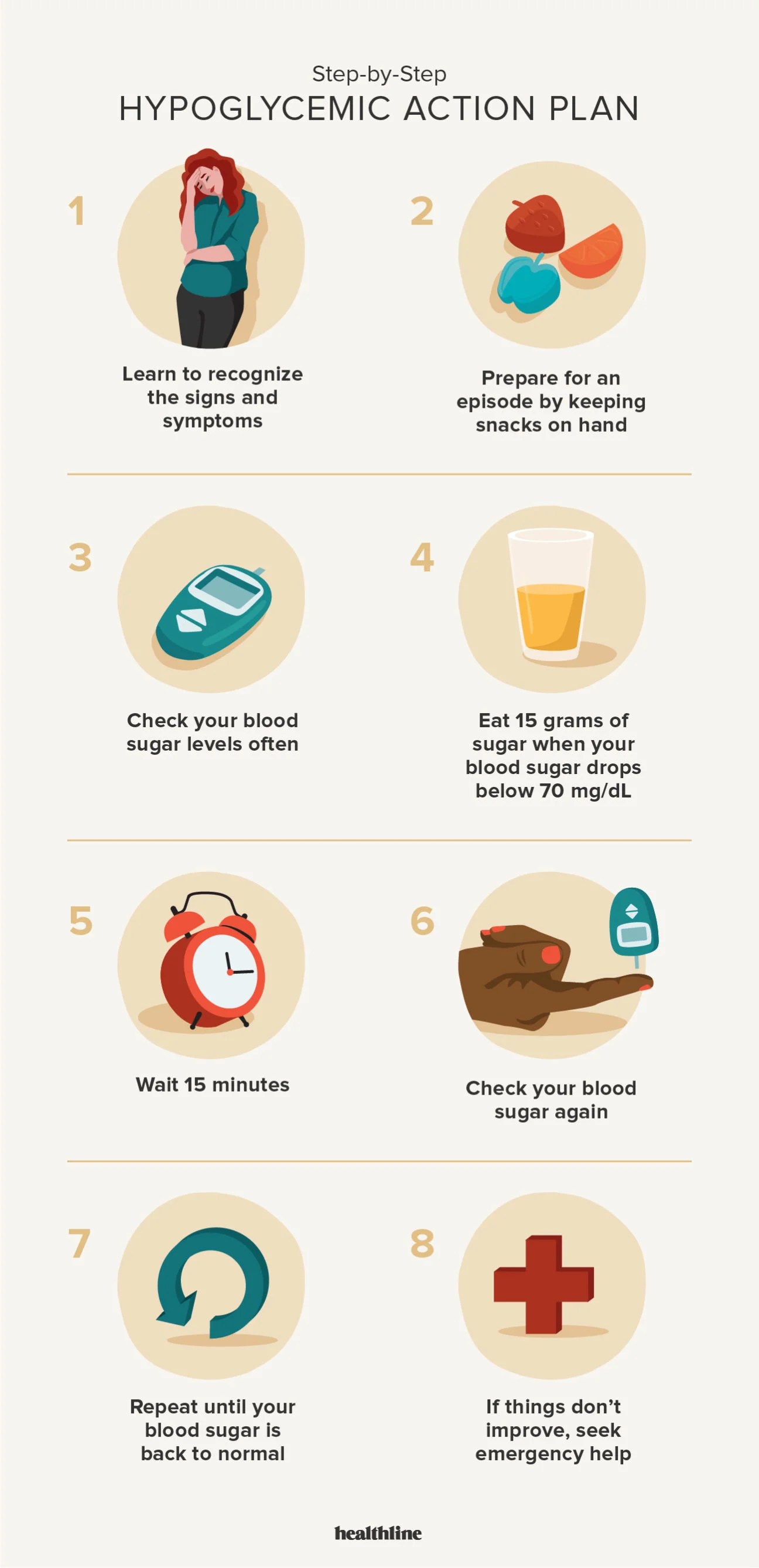
Recognizing hypoglycemia symptoms is essential for preventing severe episodes. Common signs include dizziness, shakiness, confusion, and excessive sweating. Individuals should always carry quick energy foods with them, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice, to address an emergency swiftly. Incorporating symptom relief for low blood sugar techniques, from eating regularly to assessing your daily routine can empower those living with hypoglycemia. Furthermore, creating a supportive network of online support groups can provide emotional support in managing dietary transitions.
Community Resources and Supports
Utilizing community resources can greatly ease the challenges faced in maintaining a low blood sugar diet. Seeking out nutrition education programs, advocating for nutritional needs, and involving friends and family in food planning can cultivate an open dialogue about healthy dietary choices. Supermarket shopping tips—such as learning to read nutritional labels and understanding hidden sugars—allow for informed food selections that align with dietary goals. Collaborating with support systems can sustain a healthy atmosphere ideal for maintaining balanced nutrition.
Adjusting to Social Situations and Dining Out
Lastly, managing dietary preferences in social situations can be challenging, but with creativity and planning, dining out doesn’t have to derail progress. Websites and apps focusing on dietary accommodations, as well as leveraging restaurant menus to identify meal timings and blood sugar, can enhance the dining experience. Requesting meal adjustments that guarantee low sugar levels while enjoying outings with friends can foster social interactions without compromising health goals. With proper planning and meal timing recommendations, hypoglycemia management can seamlessly merge with social aspects of life.
Key Takeaways
- Optimizing your hypoglycemia diet involves understanding the glycemic index and incorporating low GI foods into your meals.
- Create balanced meals by combining proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates to stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Consistency—both in meal timing and frequency—is essential for effective management.
- Staying hydrated and embracing mindful eating strategies can significantly reduce the risk of hypoglycemic episodes.
- Utilize community resources and support systems for better educational opportunities and emotional aid during dietary changes.
FAQ
1. What are the best foods to avoid with hypoglycemia?
To prevent symptoms, avoid high-sugar foods and highly processed snacks as they can cause rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Look out for sugar-laden options and excessive carbohydrates that can lead to **sugar spikes**. Better choices include whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats that provide sustained energy.
2. How can I create a balanced breakfast for hypoglycemia?
A balanced breakfast for hypoglycemia should include complex carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats. Options like oatmeal topped with berries and nuts or scrambled eggs with whole-grain toast can provide a nutrient-dense start to your day. This ensures stable energy levels and helps in **preventing hypoglycemia** throughout the morning.
3. What role does hydration play in managing blood sugar levels?
Hydration plays a vital role in overall metabolic functions, including blood sugar control. Keeping properly hydrated helps enhance nutrient absorption and maintain balanced blood sugar levels; thus, aim for adequate water intake daily. Be mindful of beverages that can contribute to dehydration.
4. What is the significance of mindful eating for hypoglycemics?
Mindful eating fosters awareness of hunger and fullness cues, improving self-regulation and food choices. By embracing **mindful eating techniques**, individuals can better prevent episodes of low blood sugar through conscious meal spacing and nutritional value assessments of foods consumed.
5. How can community resources help in living with hypoglycemia?
Community resources such as support groups and educational programs provide valuable insights into managing hypoglycemia. These networks can enhance understanding of **dietary guidelines** and connect individuals for shared experiences, thereby promoting emotional support during dietary adjustments.
6. What should I include in my snacks for low blood sugar?
Snacks for low blood sugar should ideally combine fats, proteins, and fiber. A handful of nuts, cheese slices with whole grain crackers, or Greek yogurt with fruit can serve as excellent options that maintain stable blood sugar and provide lasting energy.
7. What is the grazing strategy for hypoglycemia?
The grazing strategy involves consuming smaller portions of food more frequently throughout the day. This strategy helps maintain steady blood sugar levels and prevents extreme fluctuations, which can lead to **hypoglycemic episodes**.