Smart Ways to Modify Your Gastroparesis Diet for Better Digestion in 2025
Smart Ways to Modify Your Gastroparesis Diet for Better Digestion in 2025
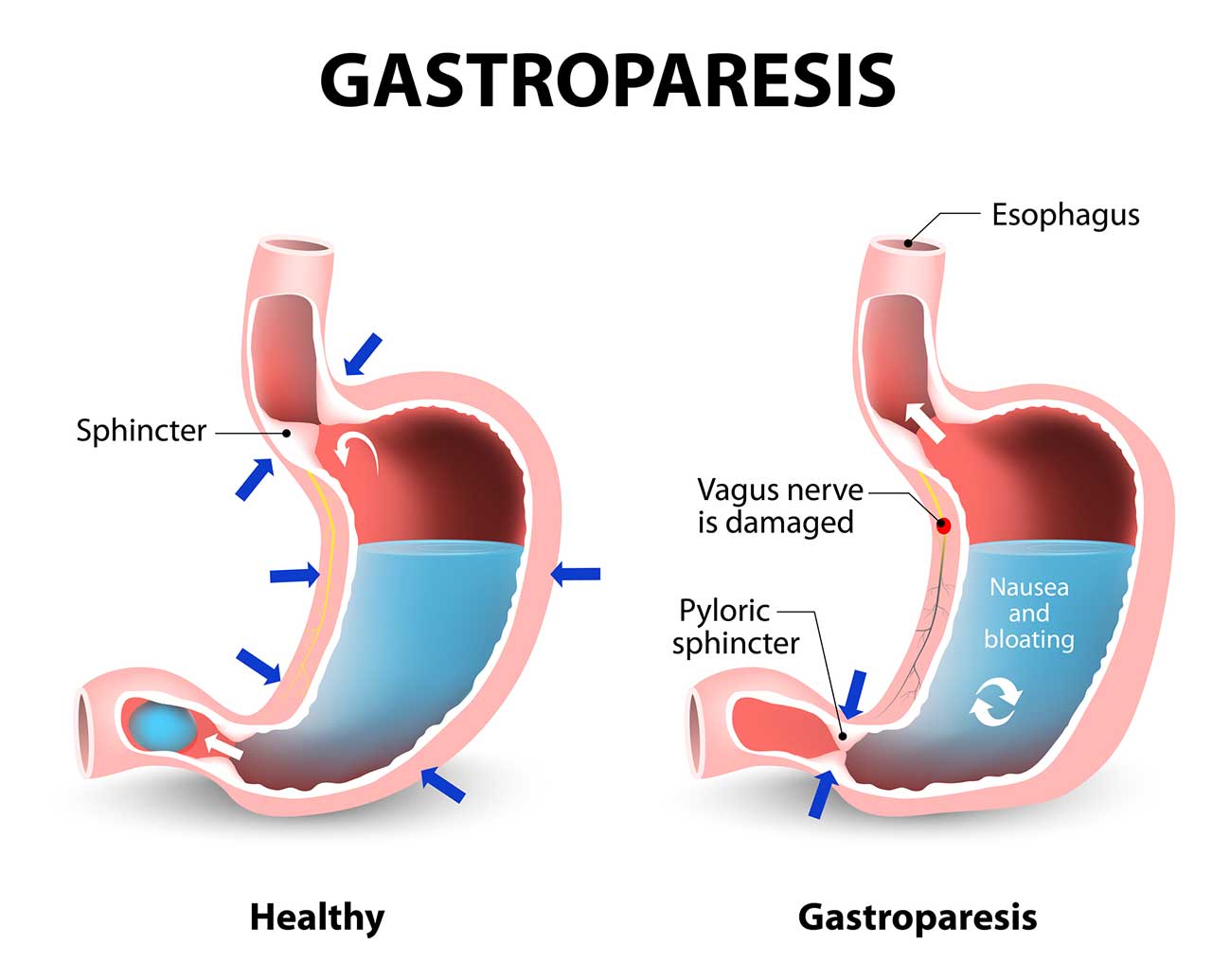
For individuals living with gastroparesis, dietary choices play a crucial role in managing symptoms and maintaining digestive health. Understanding how to effectively modify your gastroparesis diet can make all the difference. This article explores various strategies, including diet modification for gastroparesis, meal planning, and food preparation methods that improve digestion while considering personal preferences and nutritional needs in 2025.
Understanding the Gastroparesis Diet
The first step in managing gastroparesis effectively is grasping the fundamentals of a well-balanced gastroparesis diet. This diet typically focuses on smaller, more frequent meals which help alleviate symptoms and promote better nutrient absorption. Utilizing a low-fiber diet is often recommended, as it reduces the workload on the stomach and helps minimize symptoms like nausea and bloating.
Why Small Frequent Meals Matter
Implementing small frequent meals can significantly improve digestive comfort for individuals with gastroparesis. Instead of three large meals, about 5-6 smaller meals distributed throughout the day are advised. This approach allows for easier digestion and helps prevent feelings of fullness or discomfort. For instance, having a light breakfast with a smooth yogurt and a piece of fruit can provide essential nutrients without overwhelming the digestive system. Over time, adjusting portion sizes can also help gauge personal limits, promoting gradual adaptation.
Importance of Liquid Diets
A liquid diet can sometimes offer relief from discomfort associated with solid foods. Incorporating broths, smoothies, or protein shakes can simplify the digestion process and provide essential calories. When choosing liquids, ensure you select high-protein meals such as milk or dairy-based smoothies enriched with protein powder, which helps in meeting your caloric and nutritional needs without excessive fiber that might worsen symptoms.
Cooking Tips for Easy Digestion
Considering cooking methods for gastroparesis, opt for steaming or boiling rather than frying. These methods create softer and easily digestible foods. For example, preparing mashed potatoes with low-fat milk smoothens texture while adding nutrition. Making alterations to food texture can further assist in catering to individual dietary restrictions comfortably. Avoiding gas-producing foods like beans, and certain cruciferous vegetables, can also aid in reducing abdominal discomfort.
Nutritional Modification Strategies
Tailoring your diet extends beyond meal frequency. Focusing on both macronutrient distribution and nourishing ingredients can create a positive impact on digestive health. Emphasizing nutritional supplements and ensuring adequate vitamin and mineral intake strengthens the nutritional base of your meals.
Importance of Hydration Strategies
Maintaining hydration is critical in managing gastroparesis symptoms. When meal planning, incorporate a combination of water-rich foods along with your regular liquids. This ensures your body stays hydrated, which aids digestion. Strategies like keeping a water bottle on hand and sipping throughout the day can promote consistent fluid intake. Aim for hydration-focused snacks, such as homemade smoothies, combining fruits with yogurt or milk followed by a careful alteration to their texture if needed.
Macronutrient Balance: Carbs, Fats, and Proteins
Focus on a balanced diet comprising appropriate macronutrients. Incorporate a low-carbohydrate diet to help manage post-meal symptoms. This slight adjustment can reduce uncomfortable feelings associated with heavy carb meals. Instead, incorporate lean protein sources such as chicken and fish, while also ensuring you limit fatty foods, since they may slow gastric emptying. Use calorie-dense snacks to increase caloric intake without increasing food volume, like nut butters and avocados.
Managing Symptoms Through Lifestyle Changes
Addressing lifestyle factors can drastically improve overall well-being. Simple behavioral changes combined with dietary modifications lead to favorable outcomes for managing symptoms related to gastroparesis.
Meal Timing and Frequency
Adjusting meal timing is essential; try to consume your meals at the same times every day. This can train your body’s digestive clock, ultimately improving digestive function. Additionally, eating piecemeal (consuming smaller portions) may help in managing nausea during or after meals. Strive to eat in a calm, relaxed environment to help facilitate better digestion.
Environmental and Behavioral Adjustments
Reduce stress as it has been recognized to impact the digestive process negatively. Gentle exercises, when appropriate, promote circulation and can aid digestion if done after meals. Moreover, integrating mindful eating into your routine, paying close attention to hunger and satiety cues, aids not only in managing symptoms but also in the implementation of effective portioned control.
Utilizing Food Journals
Maintaining a food journal can significantly contribute to tracking food intake and identifying potential triggers. Writing down everything eaten allows insights into how various meals influence your symptoms. Utilize this journal to document symptoms after specific foods which can help to facilitate conversations with your healthcare provider or nutritionist.
Creating a Gastroparesis-Friendly Recipe Library
Creating and compiling gastroparesis-friendly recipes can not only streamline meal preparation but also alleviate stress around cooking. Adapting familiar recipes by modifying ingredients can allow you to maintain culinary preferences without distress.
Sample Recipe Modifications
When it comes to recipe adjustments, swapping whole grains for more refined versions and grams of cheese for low-fat options could significantly alter the digestibility of the dish without sacrificing flavor. Experiment with sauces, add herbs for flavor instead of raw veggies, and make use of natural broths and liquids in cooking whenever achievable. Following cooking tips specific to gastroparesis, such as removing skins and seeds, making customization easier.
Engaging with Community Resources
Participating in forums or support groups can provide a wealth of knowledge from others with similar gastroparesis lifestyle changes. Online communities offer insights on how others navigate their diets and lifestyle modifications. Many share recipes, nutrition advice, and health tips that can guide your journey toward improved health.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Consult with dietary professionals who specialize in medical diets for personalized guidance related to your unique nutritional needs. Regular check-ins or planned sessions can ensure continued progress and successful adaptation of meal styles that benefit your health.
Key Takeaways
- Small frequent meals contribute to better symptom management.
- Incorporating nutritional supplements can meet dietary restrictions targeting deficiency.
- Maintaining hydration with fluid-rich meals aids digestion.
- Meal timing and manageable portion sizes can significantly improve comfort.
- Always consult with nutrition professionals for advanced meal plans.
FAQ
1. What are some foods to avoid on a gastroparesis diet?
Some foods that are often advised against include fiber-rich foods like whole grains and raw vegetables, fatty foods such as fried items, and carbonated beverages. They can exacerbate symptoms by increasing feelings of fullness or discomfort, slowing digestion further.
2. How can I ensure proper hydration?
Staying hydrated can be achieved through beverages such as water, broth, and low-fiber smoothies. Keeping a hydration schedule that incorporates sipping fluids consistently throughout the day can also make a significant difference in managing symptoms while maintaining digestive health.
3. Are there any nutrient-dense snack options?
Yes, try snacks such as yogurt, smoothies, cottage cheese, and refined crackers. These items not only fulfill dietary appeasement but also provide balanced nutrition and higher caloric density which supports caloric goals without increasing meal sizes.
4. How important is meal planning for gastroparesis?
Meal planning is crucial as it allows for structure in the dietary approach. Focusing on ingredient preparation, nutritional balance, and managing symptoms becomes substantially more effortless. Being proactive with pre-prepared meals also reduces the likelihood of poor food choices during fatigue.
5. Can emotional health affect my gastroparesis symptoms?
Absolutely! Higher stress levels can lead to symptom flare-ups. Incorporating stress management techniques like mindfulness, gentle exercises, or even counseling can positively influence both emotional and digestive health, ultimately leading to better nutrition patterns.